Precision Tape Magnetization Leads to Precision Position Measurement
Precision Tape Magnetization Leads to Precision Position Measurement
The key to ultimate accuracy for any magnetic linear encoder system is the precision of the magnetic encoding on the tape (sometimes called a scale). Sensors inside the encoder read head respond to the strength and position of the magnetic flux coming from the magnetic poles encoded onto the tape. Precise placement of these poles – and just as importantly, the precise shape of these poles – is critical to the ultimate level of accuracy that can be delivered by the encoder system. Any inaccuracy in the position, strength, or shape of these fields will directly influence the accuracy of the encoder’s indicated position. This effect is amplified with increasing gap distance between the tape and the encoder read head. The further away from the tape, the weaker and more indistinct the shape and position of the magnetic poles becomes.
Not All Magnetic Tapes Are Created Equal
Many magnetic encoder tapes on the market are surface magnetized utilizing the conventional parallel magnetization process. This is a straightforward technique that results in an encoder tape that meets performance specifications at close gap settings between the read head and the tape.
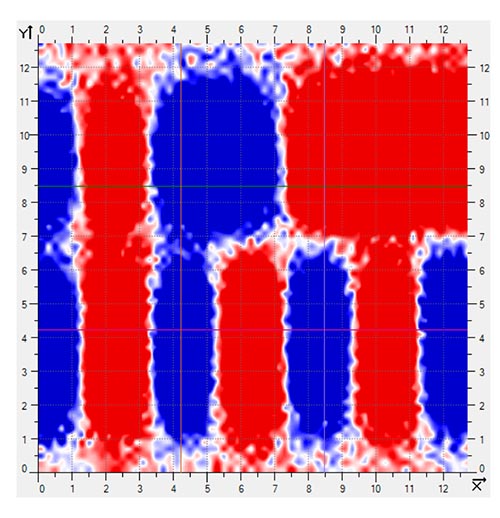
A more recent tape magnetization process called Permagnet® produces magnetic poles with improved control over their strength, shape, and location on the tape. The best way to appreciate the advantages of this technology is to compare magnetic scans of some conventionally magnetized tapes to some examples of tapes encoded with the Permagnet® process. Note the visible difference in sharp definition of the magnetic poles that is produced by the newer technology.
Conventionally Magnetized Tape – Sample #1

Tape Magnetization with Permagnet® Technology – Sample #2
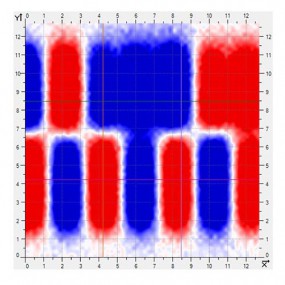
The stronger, more sharply-defined magnetic poles produced by Permagnet® technology enables encoders to be more tolerant of variation in the working distance between the encoder read head and the tape. Reduced dispersion and distortion of the magnetic fields at any distance within the specified working range reduces the influence of distance variation on the accuracy of the position measurement in real-world applications.
Summary of Application Benefits
- Improved linearity at close working distances for ultimate system accuracy
- Improved linearity at longer working distances
- Higher tolerance to deviations in the working distance, with reduced non-linearity
- Less need to closely control the working distance in the application, saving cost by reducing painstaking setup and alignment effort
- Full system accuracy, even if gap distance varies during operation
- Better linearity for any given pole spacing on the tape